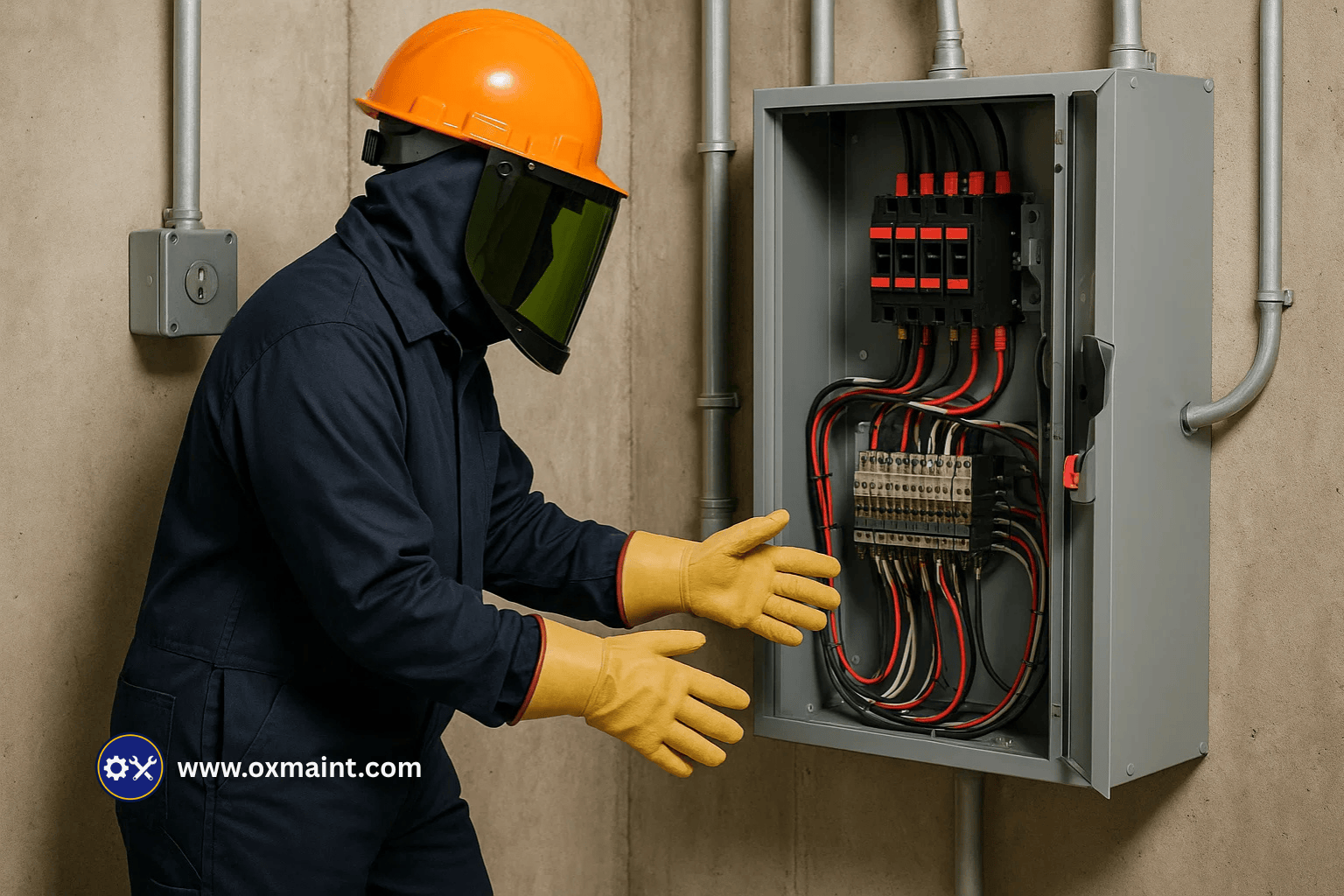
Electrical hazards remain one of the leading causes of traumatic workplace injuries and fatalities in industrial settings, accounting for over 8% of serious injuries annually (OSHA 2024). Compliance with OSHA electrical safety standards not only reduces exposure to shock and arc flash incidents but also fosters a culture of safety and operational excellence across all levels of an organization. By understanding the regulatory framework—covering requirements from 29 CFR 1910.301 through 1910.308—employers can implement robust prevention strategies, from hazard identification to worker training. This comprehensive guide outlines the critical steps to achieve and maintain full compliance with OSHA's electrical safety regulations.
The consequences of non-compliance extend far beyond potential fines ranging from $14,502 to $145,027 per violation. Electrical incidents can result in devastating injuries, production shutdowns, and irreparable damage to company reputation. Yet many organizations struggle with fragmented safety programs that fail to address the comprehensive scope of OSHA's electrical safety requirements.
Facilities implementing systematic OSHA compliance programs achieve 85% reductions in electrical incidents while improving operational reliability and worker confidence. The difference lies in treating electrical safety as an integrated system rather than isolated procedures—combining hazard assessment, worker training, equipment maintenance and documentation into a cohesive safety framework that protects both people and operations.
Ready to achieve comprehensive OSHA electrical safety compliance?
Stop risking catastrophic incidents and massive penalties. Join facilities achieving 85% incident reductions through systematic compliance programs that protect workers and operations.
Understanding OSHA Electrical Safety Regulations Framework
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets forth a detailed regulatory framework to protect workers from electrical hazards, including shock, electrocution, and arc flash incidents. This framework is codified primarily under Title 29 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) at Part 1910, Subpart S, which covers electrical standards for general industry. Within these requirements, employers are mandated to design electrical systems in accordance with the National Electrical Code (NEC), maintain equipment in safe operating condition and ensure that only qualified personnel perform energized electrical work.
In addition to structural and equipment requirements, OSHA's regulations emphasize hazard assessment, preventive maintenance, and worker training. Employers must perform regular inspections of electrical equipment for signs of deterioration—such as frayed insulating materials, exposed wiring, or damaged protective devices—which can all contribute to arc flash events. Failure to adhere to minimum clearance distances and protective grounding protocols can result in severe injuries or fatalities.
Design Requirements
Systems per NFPA and NEC guidelines
- Proper electrical system design standards
- National Electrical Code compliance
- Protective grounding protocols
- Minimum clearance distance requirements
Equipment Maintenance
Routine inspections and testing protocols
- Regular equipment condition assessments
- Insulation resistance testing
- Protective device calibrations
- Thermal imaging inspections
Work Practices
Energized work restrictions and safety procedures
- Qualified personnel requirements
- Documented safety procedures
- Personal protective equipment standards
- Energy isolation protocols
Training Requirements
Comprehensive safety education programs
- Role-specific training curricula
- Competency assessment protocols
- Refresher training schedules
- Emergency response procedures
Conducting Comprehensive Electrical Hazard Risk Assessments
A thorough hazard assessment begins with identifying potential arc flash and electrical shock sources in the work environment. Common risk factors include exposed energized conductors, pinhole leaks in insulation, and damaged programmable logic controller (PLC) enclosures. Visual inspections of switchgear, circuit breakers, and disconnects should be supplemented with infrared thermography and ultrasonic detection to uncover hidden hotspots and partial discharge events.
In addition to equipment-related hazards, environmental conditions such as humidity, dust accumulation, and corrosive atmospheres can exacerbate electrical risks. Work areas near chemical processing vessels or outdoor substations require specialized enclosures and weatherproofing measures. By cataloguing each potential shock hazard and rating the severity of exposure, safety teams can prioritize mitigation strategies and allocate resources to high-risk zones effectively.
| Assessment Type | Detection Method | Frequency | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Flash Analysis | IEEE 1584 calculations | Every 5 years | Incident energy levels, PPE selection |
| Thermal Imaging | Infrared thermography | Quarterly | Hotspot detection, connection issues |
| Visual Inspections | Physical examination | Monthly | Damaged insulation, wear identification |
| Environmental Assessment | Condition monitoring | Annually | Humidity, dust, corrosion impacts |
Implementing Lockout/Tagout Procedures Effectively
Effective lockout/tagout (LOTO) protocols require a formal written program that outlines energy isolation procedures for each piece of equipment. OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.147 specifies that authorized personnel must control hazardous energy sources—including electrical, hydraulic, pneumatic, and mechanical—before maintenance or servicing activities commence. A typical LOTO procedure includes equipment shutdown, isolation of energy sources, application of lockout devices, and verification of zero-energy state through testing.
Training on LOTO procedures must be provided to authorized and affected employees, covering the identification of energy sources, proper application of locks and tags, and verification steps. Employers should maintain a detailed log of LOTO events, including individual lockout assignments and completion confirmations. Integrating digital management tools, such as mobile LOTO checklists, streamlines documentation and provides real-time visibility into ongoing maintenance work.
LOTO Implementation Process
Digital LOTO Success Story
- Major heavy-equipment manufacturer achieved 90% reduction in unauthorized energization incidents
- 30% decrease in energy isolation task completion time through mobile checklists
- Full traceability and accountability for every maintenance action
- Improved employee confidence and streamlined audit readiness
- Analytics flagged recurring equipment failures for targeted preventive maintenance
- Reduced manual paperwork allowing focus on critical maintenance tasks
Training and Competency for Electrical Safety Personnel
OSHA requires that qualified electrical workers receive training on safety-related work practices, including hazard recognition, safe approach distances, and proper use of PPE. A robust training program incorporates classroom instruction, hands-on simulations, and periodic refresher courses. Incorporating virtual reality or augmented-reality modules allows employees to practice hazard identification in realistic scenarios without exposing them to actual risks.
Employers should tailor training content to specific job roles, equipment types, and facility layouts, ensuring that employees can relate theoretical knowledge to their real-world tasks. Evaluations—such as written tests, practical demonstrations, and peer reviews—help verify that workers understand procedures and can apply them under pressure. Establishing a mentorship program pairing experienced electricians with new hires fosters knowledge transfer and reinforces a safety-first culture.
Training Program Components
- Role-specific electrical safety curriculum development
- Hands-on simulations and AR/VR training tools implementation
- Periodic refresher courses and competency assessments
- Mentorship programs between experienced and new staff
- Comprehensive training documentation and progress tracking
- Emergency response drill simulations and toolbox talks
- Digital competency tracking dashboards and reporting
Maintaining Equipment and Preventive Maintenance Schedules
Preventive maintenance schedules should be based on manufacturer recommendations, historical performance data, and regulatory requirements. OSHA mandates periodic inspections of electrical systems to detect wear, corrosion, and loose connections that could lead to failures or arc flash events. Using computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) allows safety teams to automate inspection reminders, assign tasks, and track completion.
Inspections typically include infrared thermal scans, insulation resistance tests, and verification of protective device calibrations. Following up on identified issues—such as tightening connections, replacing worn components, or adjusting voltage settings—prevents minor defects from escalating into costly unplanned outages. Establishing service level KPIs, like mean time between failures (MTBF) and mean time to repair (MTTR), helps measure the effectiveness of maintenance strategies.
Over time, electrical infrastructure may become obsolete or fail to meet evolving OSHA and NEC requirements. Proactive equipment upgrades—such as installing arc-resistant switchgear, high-integrity grounding systems, and advanced protective relays—enhance safety and reliability. Investment in modern equipment can also improve energy efficiency and reduce operational costs, providing a strong return on investment while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Documenting Compliance and Audit Preparedness Strategies
Accurate and accessible recordkeeping is vital for demonstrating compliance with OSHA electrical safety standards during inspections and audits. Employers must retain documentation of hazard assessments, training records, inspection logs, and incident reports for the duration specified in 29 CFR 1910. A centralized electronic repository simplifies retrieval, supports version control, and prevents data loss.
Records should be organized by equipment type, location, and date, enabling auditors to verify that safety protocols were followed consistently. Employers can leverage cloud-based platforms with role-based access controls to protect sensitive information and maintain data integrity. Implementing automated compliance monitoring alerts safety managers to upcoming document expiration dates and audit requirements.
Preparing for an OSHA inspection involves conducting mock audits, training employees on proper response procedures, and ensuring that all records are up to date. Companies should assign an internal compliance team to coordinate with inspectors, provide necessary documentation, and facilitate walkthroughs. Clear signage for electrical panels, PPE stations, and emergency shutdown procedures demonstrates commitment to safety compliance.
Audit Preparedness Checklist
- Centralized electronic document repository with version control
- Role-based access controls and comprehensive data security
- Automated expiration alerts and renewal notifications
- Regular internal mock audits and gap assessments
- Employee training on inspection response protocols
- Clear facility signage for electrical panels and emergency procedures
- Timely corrective action implementation and tracking
Conclusion
Complying with OSHA electrical safety standards isn't just about avoiding penalties—it's about creating comprehensive safety systems that protect workers while ensuring operational continuity. Organizations that master electrical safety compliance achieve significant reductions in incidents, improved worker confidence, and enhanced operational reliability that creates competitive advantages.
Success requires understanding that OSHA compliance represents an integrated system combining hazard assessment, worker training, equipment maintenance, and documentation. The most effective approaches treat electrical safety as a continuous improvement process rather than a one-time implementation, enabling organizations to adapt to changing conditions while maintaining safety excellence.
Implementation success depends on systematic approaches addressing regulatory requirements, technical capabilities, and organizational factors. From conducting thorough hazard assessments to implementing effective training programs, each component contributes to overall safety performance and compliance effectiveness.
The investment in comprehensive OSHA compliance programs delivers returns through reduced incident rates, improved operational reliability, and enhanced worker confidence. Organizations that treat electrical safety as a strategic capability develop competitive advantages that extend far beyond regulatory compliance.
Ready to achieve comprehensive OSHA electrical safety compliance and eliminate incident risks?
Every day without systematic compliance increases your exposure to devastating incidents and massive penalties. Implement proven safety systems that achieve 85% incident reductions while ensuring full regulatory compliance.