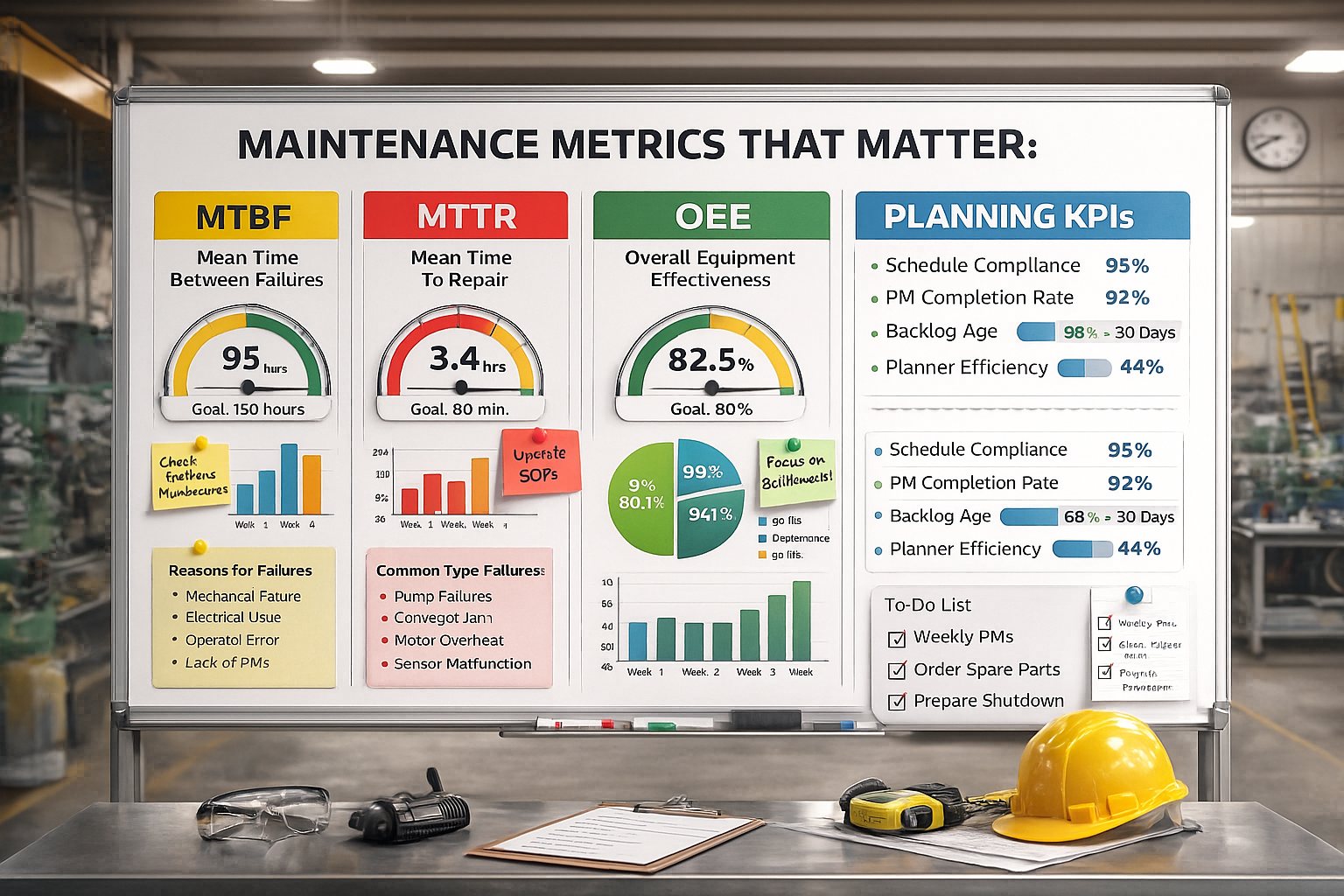
A maintenance manager reviews last month's reports: 14 equipment failures, 127 hours of unplanned downtime, $340K in lost production. But when asked "What's your MTBF?" or "What's your planned maintenance percentage?" the answers are vague estimates at best.
You can't improve what you don't measure. The right maintenance metrics transform reactive firefighting into proactive reliability management. Here are the metrics that actually drive results.
Maintenance Metrics That Matter: MTBF, MTTR, OEE & Planning KPIs
Essential KPIs for Reducing Downtime and Improving Asset Reliability
Why Maintenance Metrics Matter
Maintenance metrics provide objective data to identify problems, justify budgets, benchmark performance, and drive continuous improvement. Without metrics, you're managing by gut feel instead of data-driven decisions.
Identify Hidden Losses
Discover which assets consume the most maintenance resources and cause the most downtime
Justify Capital Investment
Use MTBF data to prove when equipment replacement is more cost-effective than continued repairs
Benchmark Performance
Compare your metrics against industry standards to identify improvement opportunities
Shift from Reactive to Proactive
Track planned vs. reactive maintenance to measure progress toward preventive strategies
The 5 Critical Maintenance Metrics
MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures)
Measures asset reliability and failure frequency
What It Measures
Average operating time between failures for repairable equipment. Higher MTBF = more reliable equipment.
How to Calculate
Industry Benchmarks
How to Improve MTBF
- Implement condition-based monitoring to catch issues early
- Upgrade preventive maintenance schedules based on OEM recommendations
- Replace worn components before failure (proactive replacement)
- Analyze failure patterns to identify root causes
MTTR (Mean Time To Repair)
Measures maintenance response efficiency
What It Measures
Average time to repair equipment after failure. Lower MTTR = faster recovery from failures.
How to Calculate
Industry Benchmarks
How to Improve MTTR
- Stock critical spare parts on-site to eliminate procurement delays
- Create standard work procedures for common repairs
- Train technicians on troubleshooting techniques
- Use mobile CMMS for faster work order dispatch and documentation
Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP)
Measures proactive vs reactive maintenance ratio
What It Measures
Percentage of maintenance work that's planned and scheduled vs. reactive emergency repairs. Higher PMP = more proactive maintenance strategy.
How to Calculate
Industry Benchmarks
How to Improve PMP
- Develop comprehensive PM schedules for all critical equipment
- Conduct failure analysis to convert reactive repairs to PM tasks
- Dedicate crew capacity for planned work (don't overcommit)
- Use backlog management to prioritize planned work over non-emergencies
Schedule Compliance
Measures planning and scheduling effectiveness
What It Measures
Percentage of planned work orders completed on schedule. High compliance = effective planning and realistic scheduling.
How to Calculate
Industry Benchmarks
How to Improve Schedule Compliance
- Plan work orders with accurate time estimates and required resources
- Lock the weekly schedule (don't allow last-minute changes without review)
- Coordinate with operations for equipment availability windows
- Track reasons for non-compliance to identify systemic issues
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)
Comprehensive measure of equipment productivity
What It Measures
Combines availability, performance, and quality to measure true productive capacity. OEE shows how much good product you're making vs. theoretical maximum.
How to Calculate
Industry Benchmarks
How to Improve OEE
- Availability: Reduce downtime through preventive maintenance and faster changeovers
- Performance: Eliminate small stops, slow cycles, and micro-downtime events
- Quality: Reduce defects through process control and better preventive maintenance
- Focus on the "Six Big Losses": breakdowns, setup/changeovers, small stops, reduced speed, startup rejects, production rejects
Track All Your Maintenance Metrics in One Place
Oxmaint CMMS automatically calculates MTBF, MTTR, PMP, Schedule Compliance, and OEE with real-time dashboards. No manual spreadsheets required.
Secondary Maintenance Metrics Worth Tracking
Maintenance Backlog
Formula: Total backlog hours / Weekly capacity
Target: 2-4 weeks of backlog
Why It Matters: Too little backlog means idle crews; too much means falling behind on critical work
PM Compliance
Formula: (Completed PMs / Scheduled PMs) × 100
Target: 95%+ compliance
Why It Matters: Skipped PMs lead to equipment failures and increased reactive maintenance
Work Order Cycle Time
Formula: Average days from WO creation to completion
Target: <7 days for routine work
Why It Matters: Long cycle times indicate planning bottlenecks or resource constraints
Wrench Time
Formula: (Actual repair time / Total technician time) × 100
Target: 35-45% (world-class: 55%)
Why It Matters: Measures technician productivity; identifies time wasted on non-repair activities
Maintenance Cost as % of RAV
Formula: (Annual maintenance cost / Replacement Asset Value) × 100
Target: 2-5% depending on industry
Why It Matters: Helps justify capital replacement decisions vs. continued repair
Emergency Work Rate
Formula: (Emergency WOs / Total WOs) × 100
Target: <10%
Why It Matters: High emergency rates indicate reactive maintenance culture and poor planning
How to Start Tracking Maintenance Metrics
Start with the Big 3
Don't try to track everything at once. Begin with MTBF, MTTR, and Planned Maintenance %—these give the biggest ROI for effort invested.
Ensure Data Quality
Metrics are only useful if data is accurate. Train technicians to close work orders promptly with accurate downtime, labor hours, and failure codes.
Use a CMMS System
Manual spreadsheet tracking is time-consuming and error-prone. A modern CMMS automatically calculates metrics from work order data in real-time.
Review Metrics Weekly
Establish weekly reviews with maintenance team to discuss trends, identify outliers, and assign action items for improvement.
Focus on Trends, Not Absolutes
Don't obsess over hitting exact benchmark numbers. Focus on continuous improvement—are metrics moving in the right direction month-over-month?
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Tracking Too Many Metrics
More metrics doesn't mean better insights. Focus on 5-7 critical KPIs that drive decision-making. Avoid "dashboard overload" where metrics are tracked but never acted upon.
Ignoring Data Quality Issues
If technicians don't close work orders accurately or on time, your metrics are garbage. Invest in training and accountability before building complex dashboards.
Comparing Apples to Oranges
Don't compare MTBF across different equipment types (pumps vs. motors). Benchmark similar assets against each other, or compare your facility against industry standards for your sector.
Using Metrics to Punish, Not Improve
Metrics should drive continuous improvement, not blame individuals. If MTTR is high, investigate root causes (lack of training, poor spare parts availability) rather than blaming technicians.
Focusing Only on Lagging Indicators
MTBF and OEE are lagging indicators (tell you what already happened). Balance with leading indicators like PM compliance and schedule compliance that predict future performance.
Not Acting on Insights
The biggest waste is tracking metrics without taking action. Every metric review should result in concrete action items with owners and due dates.
Industry-Specific Benchmark Targets
| Industry | OEE Target | MTBF (hours) | MTTR (hours) | Planned Maintenance % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Assembly | 85-90% | 5,000-8,000 | 1-3 | 90-95% |
| Food & Beverage | 75-85% | 3,000-6,000 | 2-4 | 85-90% |
| Chemical Processing | 80-90% | 6,000-10,000 | 2-6 | 90-95% |
| Oil & Gas | 85-95% | 8,000-15,000 | 3-8 | 85-90% |
| Mining | 75-85% | 4,000-8,000 | 4-12 | 80-85% |
| Utilities (Power) | 90-95% | 10,000-20,000 | 2-6 | 95%+ |
Note: These are general guidelines. Your actual targets should be based on your specific equipment, operating conditions, and business objectives.
Get Your Free Maintenance Metrics Dashboard Template
Download our Excel template pre-configured with formulas for MTBF, MTTR, OEE, and all key maintenance metrics. Start tracking today.
Questions about implementing maintenance metrics? Chat with our team — Get help setting up KPI dashboards in your CMMS.
Key Takeaways: Maintenance Metrics Best Practices
- Start with the Big 5: MTBF, MTTR, Planned Maintenance %, Schedule Compliance, and OEE
- MTBF measures reliability (higher is better); MTTR measures repair speed (lower is better)
- Aim for 90%+ planned maintenance to shift from reactive to proactive maintenance culture
- World-class OEE is 85%+ combining availability, performance, and quality
- Use a CMMS to automate metric tracking instead of manual spreadsheets
- Review metrics weekly and assign concrete action items for continuous improvement
Automate Your Maintenance Metrics Today
Oxmaint CMMS tracks all critical maintenance KPIs automatically with real-time dashboards, customizable reports, and mobile access. See how it works in a 15-minute demo.