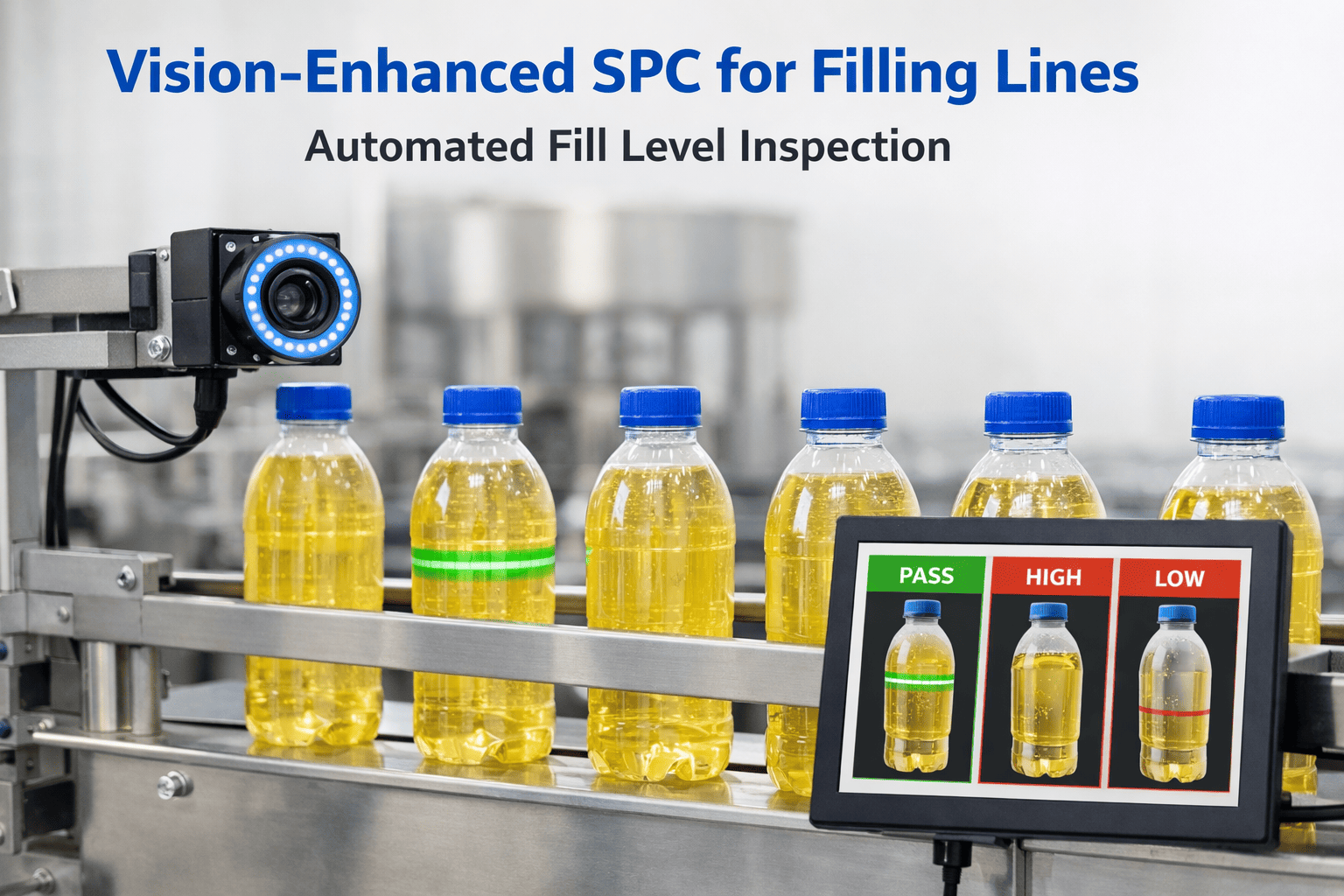
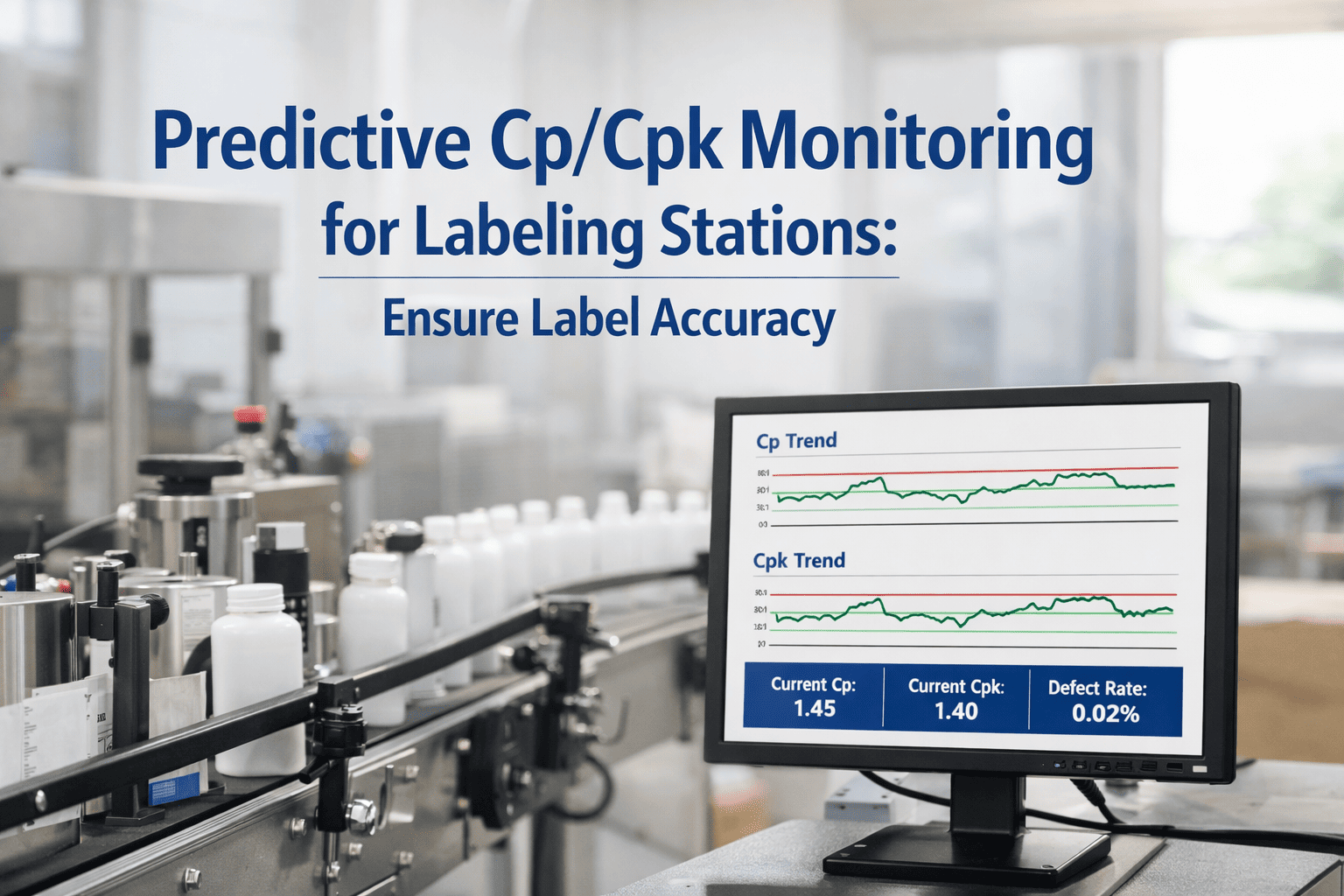
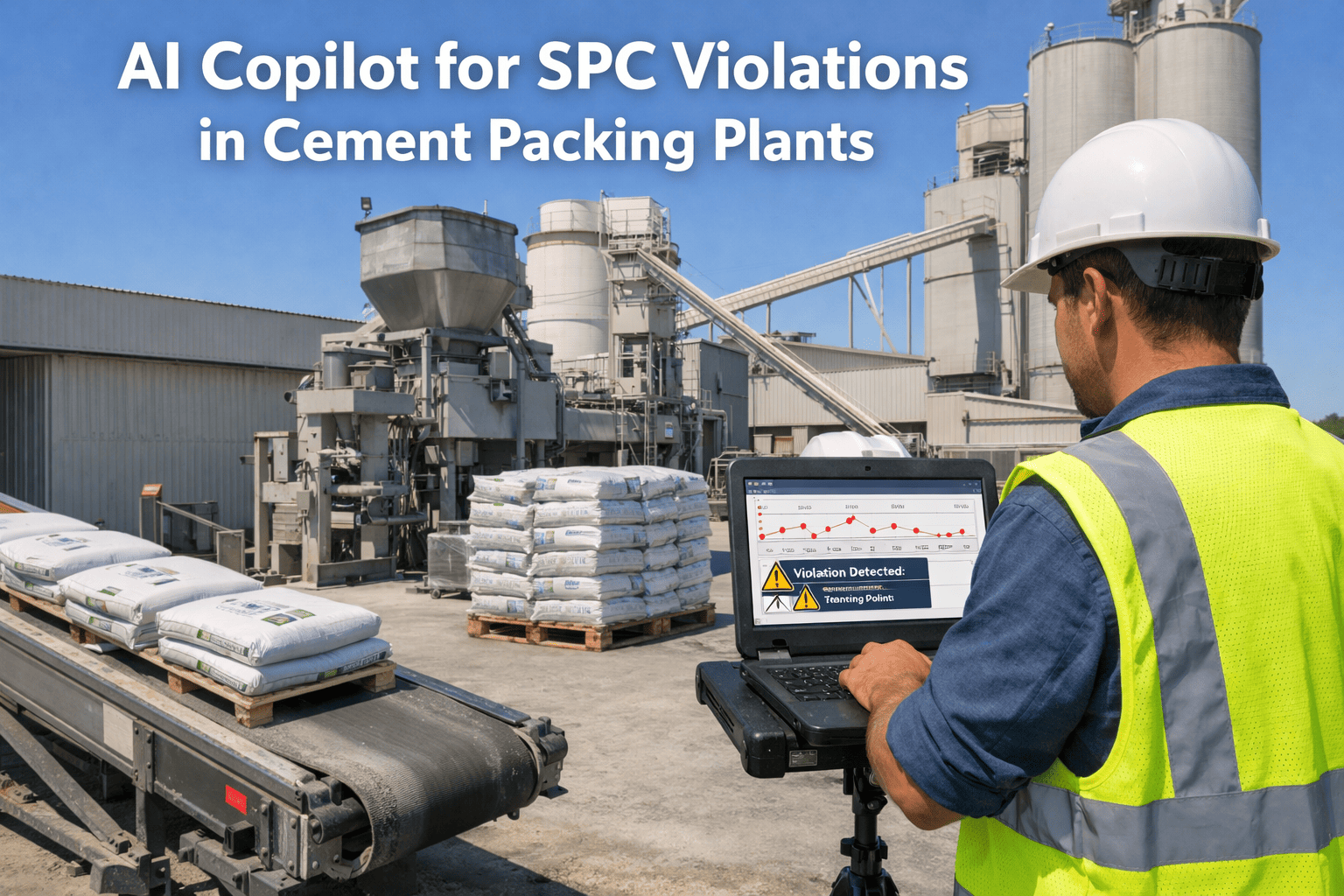
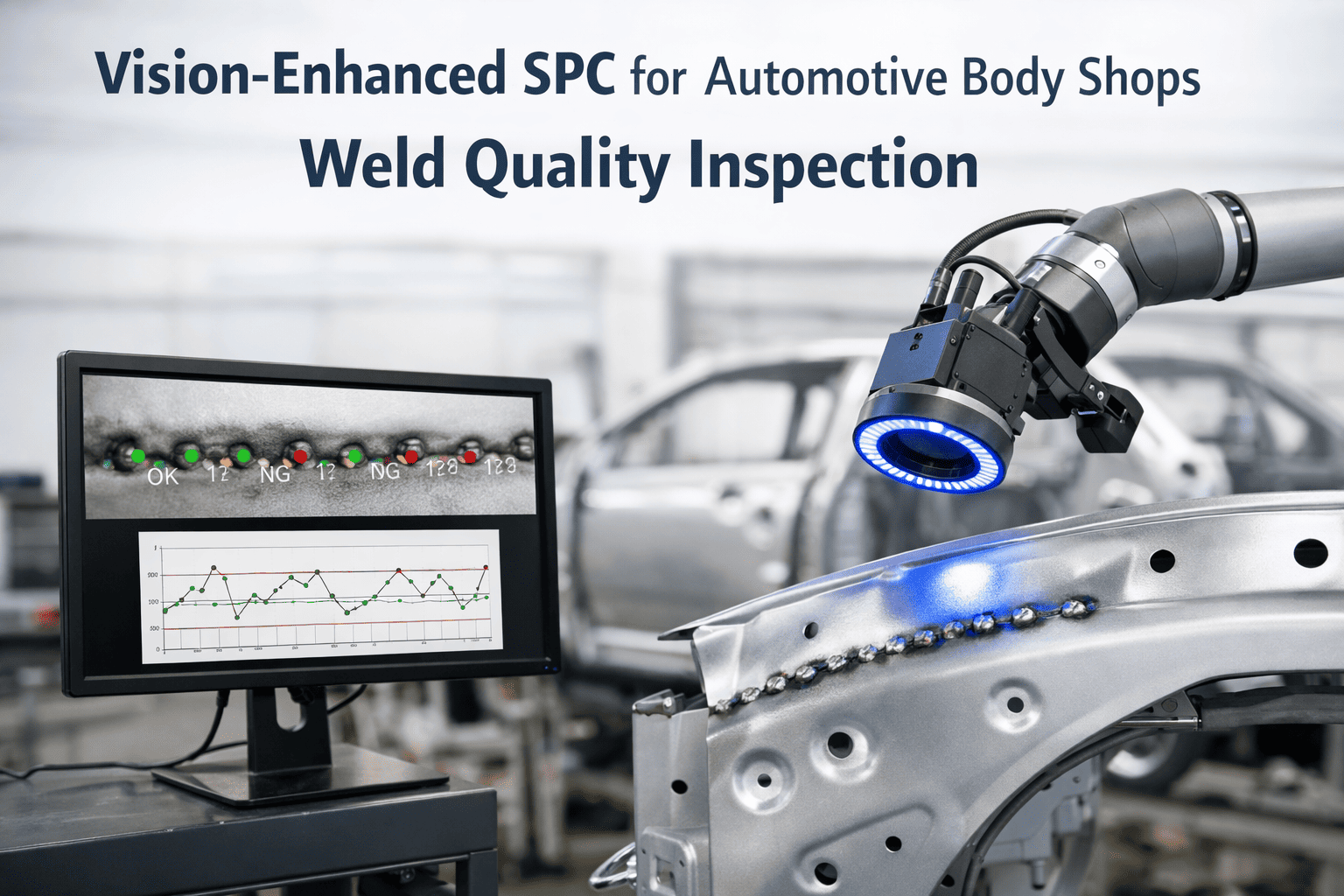
Every automotive press line tells a story through its tonnage data. The problem is, traditional SPC control charts only listen to one chapter, the historical baseline, and ignore everything else happening on the shop floor. Die surfaces erode with every stroke, incoming steel coils shift in hardness between suppliers, and press frames expand as temperatures climb through a shift. Adaptive control limits listen to the full story, recalibrating quality thresholds in real time so your SPC catches what actually matters and stops crying wolf over normal process evolution. Schedule a consultation to see how Oxmaint brings adaptive intelligence to your press line quality control.
$180K+
Annual scrap cost from static SPC blind spots on a typical 4-press tandem line
37%
False alarm reduction when switching from fixed to adaptive control limits
<5 min
Time for adaptive algorithms to recalibrate after a die change or coil swap
The Problem With Fixed Control Limits on Press Lines
Standard SPC sets control limits at three standard deviations from a historical process mean. That works beautifully in a textbook, but automotive press lines are not textbooks. They are living systems where dozens of variables shift continuously. Fixed limits create two dangerous failure modes: excessive false alarms that train operators to ignore warnings, and missed real deviations hiding within outdated thresholds that let defective panels flow downstream to body shop and paint.
What Goes Wrong
Die wear gradually shifts tonnage upward, but fixed UCL stays the same, so the chart shows "in control" while parts slowly drift out of spec
New coil batch is harder than baseline steel, tonnage jumps, and the press line shuts down on a false alarm while perfectly good parts are scrapped
Night shift startup causes thermal drift in press frame, triggering nuisance alerts for the first 45 minutes until the machine warms up
After die regrind, tonnage profile changes slightly and operators must manually recalculate limits or run blind until engineering updates the chart
What Adaptive Fixes
Wear-aware models track cumulative die degradation and widen limits proportionally while tightening sensitivity near regrind intervals
Material batch properties are factored in automatically so expected tonnage ranges shift with legitimate coil-to-coil variation
Thermal compensation models learn each press's warm-up curve and suppress false alerts during known transient periods
Post-regrind baselines are loaded automatically from die history, recalculating limits within minutes of the first production stroke
Stop choosing between false alarms and missed defects. Oxmaint's adaptive SPC eliminates that tradeoff by making your control limits as dynamic as your press line.
Inside the Adaptive Control Loop
Adaptive SPC is not simply recalculating averages more often. It is a contextual intelligence layer that understands why tonnage is changing, not just that it changed. Oxmaint's platform correlates tonnage sensor data with die stroke counts, material certifications, ambient conditions, and press operating parameters to build a living model of expected behavior. Here is how the loop works from sensor to decision. Sign up for Oxmaint to connect your press monitoring infrastructure to intelligent adaptive analytics.
01
Tonnage Data Capture
Strain sensors on press columns stream peak tonnage, reverse load, and full through-stroke force signatures at sub-millisecond resolution. Every stroke is recorded, not sampled.
02
Context Injection
Die ID, stroke count since last regrind, coil material grade, press speed, blankholder pressure, and ambient temperature are tagged to every tonnage reading. This transforms raw force data into context-rich process intelligence.
03
Dynamic Baseline Modeling
Machine learning models maintain a living expected-value surface across all context dimensions. Instead of one flat mean line, the model knows tonnage should be X at stroke count 5,000 with material grade Y at temperature Z.
04
Limit Recalculation
UCL and LCL are recalculated at configurable intervals or triggered automatically by process events: die changes, coil changeovers, shift transitions, or speed adjustments. Limits widen or tighten based on expected variability for current conditions.
05
Smart Alert Classification
Breaches are classified as expected wear trend, sudden anomaly, material-driven shift, or thermal transient. Operators receive root-cause context with every alert, not just a red light.
06
CMMS Work Order Generation
When adaptive limits detect die wear approaching intervention thresholds, Oxmaint automatically creates maintenance work orders, schedules regrind, and notifies tooling teams. Quality intelligence flows directly into maintenance action.
What Adaptive SPC Monitors on Your Press Line
Effective adaptive quality control requires watching multiple correlated signals simultaneously. Each parameter adds context that makes the adaptive model smarter and more precise at distinguishing real problems from normal process evolution.
Primary Signal
Peak Tonnage per Stroke
Maximum forming force each cycle is the foundational SPC parameter. Adaptive limits model expected tonnage increase from die wear and flag deviations that exceed the wear curve, catching stuck slugs, misfeeds, or die cracks within strokes rather than parts.
Signature Analysis
Through-Stroke Force Envelope
Full force-vs-crank-angle profiles compared against adaptive envelopes that account for die age and material properties. Catches forming issues that peak-only monitoring completely misses.
Wear Tracking
Die Degradation Index
Cumulative wear modeled through tonnage trend correlation, part measurements, and stroke count. Limits tighten as dies approach regrind intervals to detect accelerating wear early.
Material Intelligence
Coil Batch Compensation
Incoming steel properties, thickness, hardness, and coating, are factored into expected tonnage ranges. New coil loads trigger automatic limit adjustment to prevent false alarms from legitimate material differences.
Environment
Thermal Drift Correction
Press frame expansion from temperature changes alters shut height and tonnage readings. Models learn each machine's warm-up curve and suppress transient false alerts during startups and ambient shifts.
Workforce
Cross-Shift Performance Baseline
Separate adaptive baselines for each shift reveal operator-specific patterns, setup inconsistencies, and training gaps. Rather than averaging away the differences, the system flags when one shift consistently operates outside the others' behavioral envelope.
See these parameters in action on a live press line dashboard. Our engineers will walk you through real-time adaptive monitoring configured for your specific stamping operation.
Adaptive Configuration by Press Type
Different press configurations demand different adaptive strategies. A progressive die press accumulating 200 strokes per minute has fundamentally different wear dynamics than a hydraulic press running deep-draw operations at 8 cycles per minute. Oxmaint configures adaptive models specific to your equipment and process.
Adaptive SPC Configuration by Press Type
Measurable Impact on Press Line Operations
Automotive stamping plants deploying adaptive SPC through Oxmaint's CMMS report compounding returns across quality, uptime, and die maintenance. The improvements are not theoretical; they emerge from eliminating the systemic waste created by static control limits.
Fewer false SPC alarms, meaning operators trust and respond to the alerts that remain
Reduction in press-related scrap through earlier, more accurate defect detection
Longer die life by scheduling regrinds based on actual wear data, not fixed stroke counts
Real anomalies caught before defective panels leave the press shop floor
Model your press line savings. Create a free Oxmaint account and our stamping quality specialists will calculate your adaptive SPC ROI based on your actual scrap and downtime data.
From Installation to Production in 7 Weeks
Deploying adaptive SPC does not require ripping out your existing tonnage monitors or rewriting your quality systems. Oxmaint layers adaptive intelligence on top of your current infrastructure through a proven phased approach. Book a demo to get a deployment timeline customized for your press shop.
Week 1-2
Connect and Capture
Interface Oxmaint with existing tonnage monitors (Helm, Link, Wintriss, Toledo). Capture baseline signatures for each die set. Map material batch data and historical stroke counts.
Week 3-4
Model and Calibrate
Train adaptive models on historical tonnage, wear, and material data. Calibrate die wear curves for each die family. Configure alert classification rules and operator notification preferences.
Week 5-6
Validate Side-by-Side
Run adaptive SPC in parallel with existing static charts. Compare alert accuracy, false alarm rates, and defect catch rates. Refine thresholds with operator and quality team feedback.
Week 7+
Go Live and Expand
Switch to adaptive SPC as the primary quality system. Enable automatic CMMS work order generation on wear-triggered events. Expand monitoring to additional press lines and parameters.
In automotive stamping, your dies are aging every stroke, your material varies coil to coil, and your presses shift with temperature. Static control limits pretend none of that is happening. Adaptive SPC acknowledges reality and adjusts accordingly, which is why it catches defects that matter and ignores the noise that does not.
-- Automotive Stamping Quality Engineering Director
Make Your Press Line SPC as Smart as Your Press Line
Your fixed control charts cannot distinguish between normal die wear and a cracked insert, or between a harder coil batch and a misfeed event. Oxmaint's adaptive SPC monitors every stroke in context, recalibrates limits automatically with every die change and material switch, and triggers maintenance work orders the moment quality trends demand action. Transform your press line quality from reactive firefighting to predictive precision.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does adaptive SPC handle die changes without generating startup false alarms?
When a die change event is detected through PLC signals or operator input, Oxmaint automatically loads the stored baseline profile for the incoming die set and recalculates control limits based on that specific die's wear history combined with the current material batch. This eliminates the startup noise that plagues static SPC after every changeover.
Book a demo to see die-change automation in action.
Can adaptive SPC integrate with our existing tonnage monitoring hardware?
Yes. Oxmaint integrates with all major tonnage monitoring systems including Helm, Link, Wintriss, and Toledo through standard industrial protocols like Modbus, OPC-UA, and Ethernet/IP. Your existing strain sensors and monitors continue operating while Oxmaint adds the adaptive intelligence layer on top.
What happens when a new material batch causes unexpected tonnage variation?
The adaptive model recognizes material batch changes through incoming quality data or coil ID tracking and automatically adjusts expected tonnage ranges. This prevents false alarms while maintaining full sensitivity to genuine forming anomalies within that material's expected behavior range.
Sign up for a free account to explore material-aware SPC configuration.
Does this satisfy IATF 16949 SPC documentation requirements?
Oxmaint automatically generates all SPC documentation required by IATF 16949 including timestamped control charts, limit calculation records, out-of-control action reports, and process capability studies. Every adaptive limit change is fully logged with a justification trail, satisfying auditor requirements for traceability and rational subgrouping.
How quickly will we see measurable results after deployment?
Most automotive stamping plants see measurable false alarm reduction within the first two weeks of parallel operation. Scrap reduction and die life improvements typically become statistically significant within 60 to 90 days as adaptive models accumulate enough data to consistently outperform static baselines.
Schedule a consultation to discuss expected timelines for your operation.