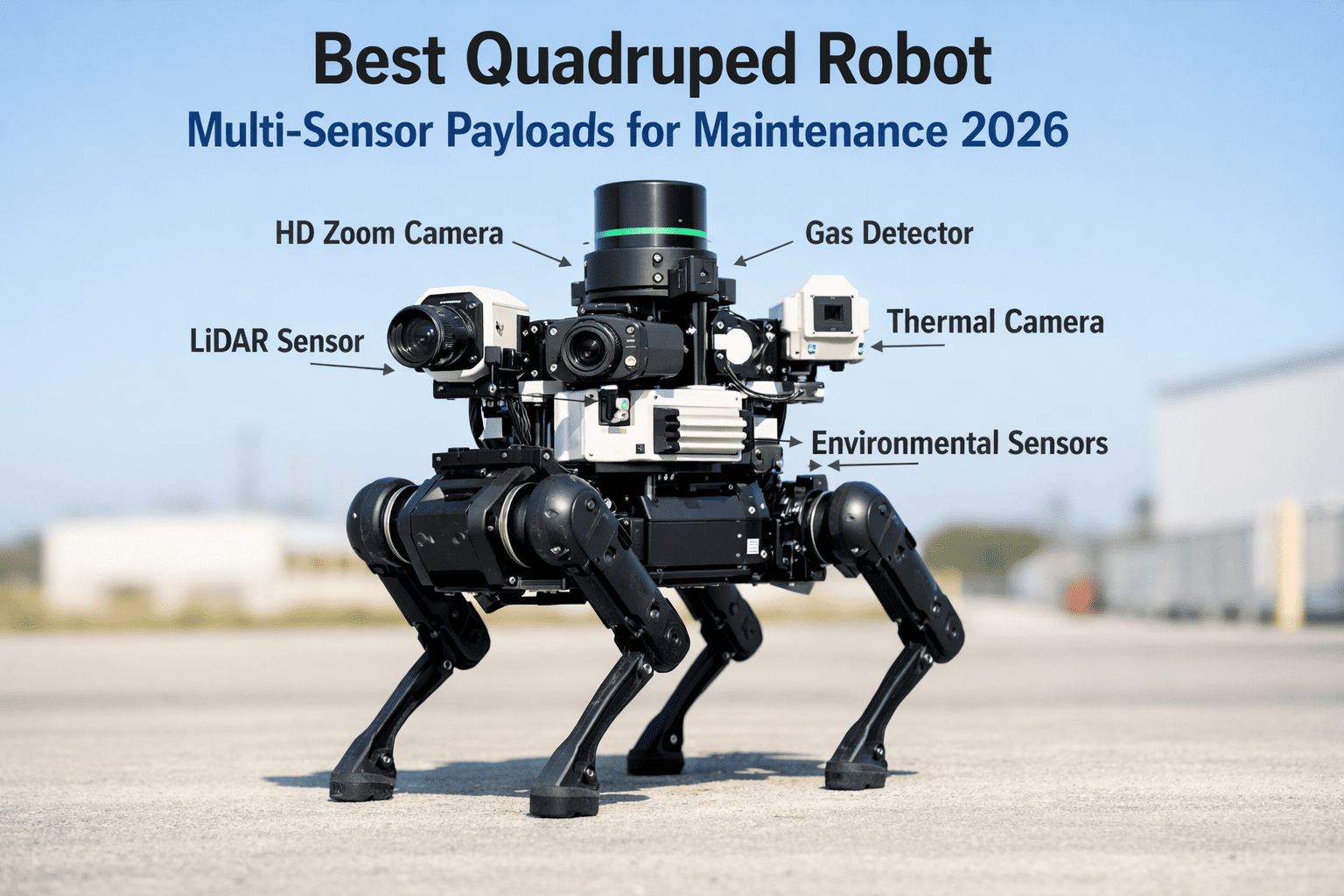
Industrial facilities worldwide are deploying quadruped robots for inspection, patrol, and hazardous-zone monitoring at an unprecedented pace. The global industrial quadruped robot market reached $2.2 billion in 2025 and is projected to surpass $9.9 billion by 2033, growing at over 20% annually. Yet safety frameworks have not kept up. Existing standards were designed for stationary arms and wheeled vehicles—not for machines that walk, balance dynamically, and can collapse unpredictably. If your facility is deploying or evaluating robot dogs for inspection, understanding the evolving safety landscape is not optional—it is the difference between a compliant operation and an OSHA citation. Schedule a free demo to see how Oxmaint manages robot safety compliance across your facility.
What Makes Quadruped Robot Hazards Different from Traditional Industrial Robots
A robotic arm bolted inside a safety cage presents predictable, well-documented hazards. A four-legged robot walking alongside your workforce introduces an entirely different risk profile. The core distinction is dynamic stability—quadrupeds actively balance hundreds of times per second. When that balancing act fails due to power loss, software faults, or terrain obstacles, the result is an uncontrolled fall with a trajectory that depends on speed, load, floor angle, and gait phase.
Traditional Industrial Robots
Fixed position inside safety fences or cages
Predictable reach envelope with defined exclusion zones
Statically stable—stays in place if power is cut
Well-established standards (ISO 10218, ISO/TS 15066)
Quadruped Robots (Robot Dogs)
Mobile throughout the facility, shared human workspace
Dynamic operating envelope that changes with every step
Dynamically stable—collapses unpredictably if power fails
Standards still evolving (ISO 25785-1 under development)
This fundamental difference means your existing robot safety program likely has gaps. Fall-zone calculations, stumble-recovery hazard modeling, battery thermal management during hot-swap, and dynamic speed-separation monitoring are all new requirements that traditional risk assessments never addressed. Sign up for Oxmaint and create digital safety checklists customized for your legged robot deployment.
Applicable Safety Standards and Regulatory Framework for 2026
No single published standard covers quadruped robots comprehensively as of early 2026. Instead, compliance requires layering multiple frameworks—some recently updated, others still in draft. The table below maps the current regulatory landscape so your EHS team knows exactly which standards apply and what each one requires.
Standard / Regulation
Status
What It Covers for Quadrupeds
ISO 10218-1/2:2025
Published
Application-based risk assessment (not hardware-only), functional safety, lifecycle documentation, expanded integration requirements for all industrial robots including mobile platforms
ANSI/A3 R15.06-2025
Published
U.S. national standard with explicit functional safety requirements, risk-based collaboration mandates, and structured lifecycle coverage—first major revision since 2011
ISO 25785-1
Working Draft
First standard specifically for dynamically stable mobile robots—fall-zone formulas, balance performance metrics, level-ground stability assumptions, and legged locomotion hazards
TR R15.108
Technical Report
Detailed hazard analysis for bipedal, quadrupedal, and wheeled balancing platforms—bridge guidance until ISO 25785-1 publication expected 2026-2027
EU Machinery Regulation + AI Act + Cyber Resilience Act
In Force
Unified European framework requiring safety validation, AI system transparency, cybersecurity certification, encrypted communications, and continuous AI model auditing for connected robots
ISO 13849 / IEC 62061
Published
Functional safety of safety-related control systems—applies to emergency stops, speed-limiting functions, and safety-rated sensors integrated into quadruped platforms
How to Conduct a Risk Assessment for Quadruped Robot Deployments
A thorough risk assessment is the foundation of every compliant quadruped deployment. ISO 12100 provides the general methodology, but legged robots introduce hazard categories that standard templates do not cover. Below is a structured framework covering the six hazard domains unique to walking industrial robots.
1
Fall and Collapse Hazard
Calculate the fall-zone radius using the robot's shoulder height, mass, maximum speed, and center of gravity. Add a minimum 1-meter buffer for stumble-recovery motions. Slopes above 5 degrees require custom engineering analysis per the upcoming ISO 25785-1 guidance.
2
Locomotion Contact Forces
Model the force-impact potential of leg swing during normal gait and emergency recovery. Reference ISO/TS 15066 contact force thresholds for transient and quasi-static body contact—adapted for leg geometry rather than arm reach.
3
Battery and Thermal Management
Document thermal monitoring protocols, hot-swap procedures, and charging station placement. Lithium battery thermal runaway presents fire and toxic fume risks not present in traditional tethered robots. Track battery health and charge cycles in your CMMS.
4
Shared-Space Interaction Zones
Map every patrol route against pedestrian traffic, forklift paths, and doorway congestion points. Define dynamic speed-separation zones that contract or expand based on real-time proximity detection rather than static exclusion fences.
5
Cybersecurity and Data Integrity
Assess unauthorized access vectors—remote control hijacking, data link compromise, firmware tampering, and AI model poisoning. The EU Cyber Resilience Act mandates encrypted communications and vulnerability management for all networked industrial devices.
6
Environmental and Terrain Factors
Evaluate gait stability on wet surfaces, metal grating, gravel, and sloped terrain specific to your facility. Document IP ratings, ATEX/IECEx certifications for explosive atmospheres, and temperature operating ranges against actual site conditions.
Digitize Your Robot Risk Assessments
Paper checklists get lost. Spreadsheets fall out of date. Oxmaint converts every risk assessment into a trackable, auditable digital workflow—with automated reminders, photo evidence, and corrective action assignments built in.
Dynamic Safety Zones: From Fixed Fences to Virtual Cells
Traditional robots operate behind fixed physical barriers. Quadrupeds roam freely, making static fences impractical. The emerging approach—supported by ISO 25785-1 draft guidance—replaces physical barriers with dynamic virtual safety zones that shift in real time based on the robot's speed, heading, and sensor-detected proximity to people and obstacles.
Emergency Stop
Restricted
Speed Reduction
Awareness
Emergency Stop Zone — Immediate controlled sit-down triggered by any intrusion. Hard boundary integrated with plant alarm systems. Non-negotiable at any speed.
Restricted Zone — No personnel access during autonomous operation. Defined by maximum fall radius plus stumble-recovery buffer. Expands with higher speed.
Speed Reduction Zone — Robot automatically decelerates when sensors detect personnel. Dynamic boundary width adjusts proportionally to current walking speed.
Awareness Zone — Outer perimeter with visual status lights and audible signals communicating the robot's approach direction and operating state to nearby workers.
Why CMMS Software Is Essential for Robot Safety Compliance
Compliance documentation is what separates a safe facility from a cited one. Auditors do not ask whether you performed inspections—they ask for timestamped proof with photos, assigned personnel, and documented follow-up actions. Oxmaint automates this entire process, turning scattered safety efforts into an audit-ready compliance system. Sign up for Oxmaint to centralize all your robot safety inspections, work orders, and audit records in one platform.
Digital Risk Assessments — Create, store, and version-control every risk assessment linked directly to each robot asset. Mandatory fields ensure nothing is skipped.
Automated Inspection Schedules — Set recurring safety inspections for each quadruped—battery health checks, e-stop tests, sensor calibrations—with automatic reminders and escalation for overdue tasks.
Corrective Action Workflows — When an inspection uncovers a safety issue, Oxmaint automatically generates a work order assigned to the right technician with priority, deadline, and follow-up verification.
Incident and Near-Miss Reporting — Log every safety event with photos, location data, and root-cause analysis. Build a historical dataset that drives continuous improvement in your robot safety program.
Industry-Specific Compliance Considerations
Each industry that deploys quadrupeds faces distinct regulatory requirements, environmental hazards, and operational constraints. Your risk assessment and CMMS configuration must reflect these sector-specific demands.
Oil and Gas
Explosive atmosphere certifications (ATEX/IECEx Zone 1) are mandatory. ANYbotics ANYmal X is currently the only commercially ex-certified quadruped. All patrol routes must be documented against facility hazard zone maps and tracked through your safety management system.
Manufacturing
Shared-space operations with forklifts, overhead cranes, and production staff require ISO 10218 application-level assessments. Dynamic speed-separation monitoring and e-stop integration with existing machine safety networks are critical compliance points.
Construction
Uneven terrain, temporary structures, and falling debris create unique stability hazards. OSHA's General Duty Clause applies in the absence of robot-specific construction standards. Site-specific gait stability testing on every terrain type is essential.
Mining and Energy
Underground deployments require confined-space protocols, gas detection integration, and emergency retrieval procedures. MSHA regulations apply in U.S. mining environments. Battery management protocols must address operation in extreme temperatures.
Food and Pharmaceuticals
IP-rated enclosures for wash-down environments, FDA/HACCP compliance for hygiene-sensitive areas, and chemical compatibility testing for cleaning agents. Robot patrol data integrates with sanitation verification workflows in CMMS.
Warehousing and Logistics
ISO 3691-4 for mobile automation applies alongside pedestrian traffic management. Narrow-aisle navigation, dock-area congestion, and night-shift autonomous operation each require separate risk evaluations and CMMS-tracked safety controls.
Build an Audit-Ready Robot Safety Program Today
Standards are evolving, quadruped deployments are accelerating, and regulators are paying attention. Oxmaint gives your EHS and maintenance teams one platform to manage risk assessments, automate inspection schedules, track corrective actions, and generate compliance reports—whether you run one robot or a fleet across multiple sites.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is there a dedicated ISO standard for quadruped robot safety?
How do you calculate fall zones for a robot dog?
Fall-zone calculations use the robot's shoulder height, total mass (including payload), maximum walking speed, and center of gravity location. The base fall radius is typically the shoulder height multiplied by a safety factor, with an additional buffer of at least one meter added for stumble-recovery motions. Floor slope above five degrees requires custom engineering analysis because standard formulas assume level ground. ISO 25785-1 will standardize these calculations once published.
What OSHA requirements apply to quadruped robots in the U.S.?
How does a CMMS help with robot safety compliance?
A CMMS centralizes every safety document—risk assessments, inspection checklists, corrective action records, training logs, and audit reports—into one searchable system. It automates scheduling so inspections never fall through the cracks, assigns accountability for follow-up actions, and generates audit-ready reports on demand. This shifts your safety program from reactive paperwork to proactive digital management.
How often should risk assessments be updated for quadruped deployments?