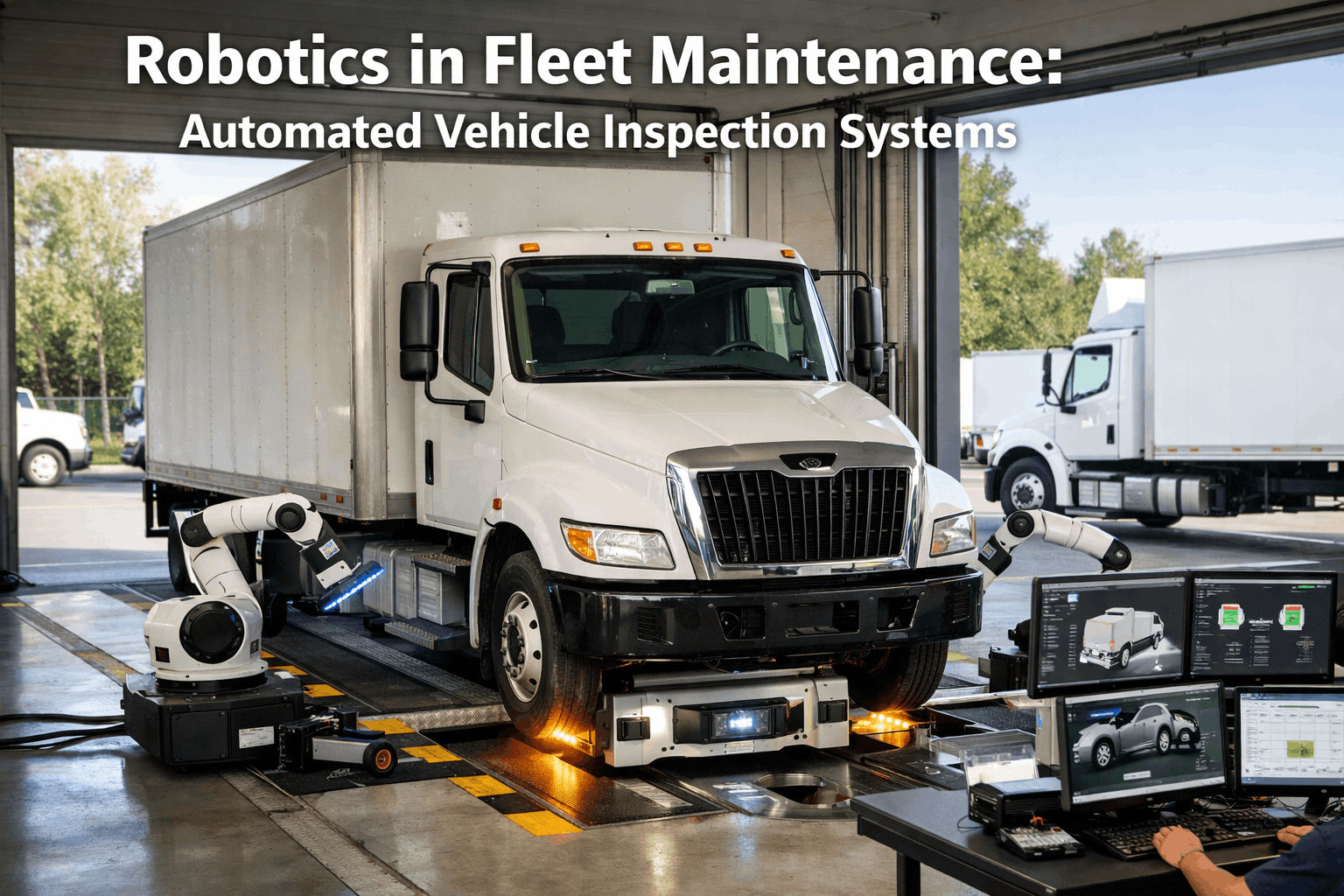
Fleet garages are on the edge of a transformation that will redefine how vehicles are inspected, diagnosed, and serviced. Autonomous maintenance robots — powered by AI, machine vision, and advanced sensor arrays — are moving from factory floors into fleet workshops, taking on the repetitive, time-consuming tasks that drain technician productivity and delay vehicle turnaround. From robotic arms that change tires and swap fluids to AI-driven inspection systems that scan an entire vehicle undercarriage in under five minutes, the technology is here and it is scaling fast. The global autonomous mobile robot market is growing at 15.3% CAGR and is projected to reach $9.26 billion by 2030, with fleet maintenance emerging as one of the fastest-growing adoption sectors. But deploying robots without a system to coordinate their work, track their output, and integrate with your existing maintenance workflows creates chaos instead of efficiency. That is where CMMS integration becomes essential. Oxmaint connects your autonomous maintenance robots to your work order system, ensuring seamless task assignment, real-time reporting, and complete maintenance documentation. Sign up for Oxmaint and build the fleet garage of the future today.
What Are Autonomous Maintenance Robots for Fleet Garages
Autonomous maintenance robots are AI-enabled machines designed to perform inspection, diagnostic, and routine servicing tasks on fleet vehicles with minimal or no human intervention. Unlike traditional industrial robots confined to manufacturing assembly lines, these systems are built to operate in dynamic workshop environments alongside human technicians, adapting to different vehicle types, service bays, and maintenance requirements. They combine multiple technologies into a single operational platform: machine vision for defect detection, robotic arms for physical servicing tasks, natural language processing for technician interaction, and IoT connectivity for real-time data exchange with fleet management systems.
In a fleet garage context, these robots are not replacing technicians — they are amplifying them. By handling the repetitive, physically demanding, and time-intensive tasks like tire mounting, fluid exchanges, undercarriage scanning, and battery health checks, autonomous robots free your skilled technicians to focus on complex diagnostics, critical repairs, and decision-making that requires human expertise and judgment. Forward-thinking fleet operators are already seeing a 40% reduction in maintenance costs and 45% decrease in equipment downtime through AI-powered maintenance automation. Book a demo to see how Oxmaint integrates robotic maintenance into your fleet workflow.
Types of Autonomous Robots Entering Fleet Garages
The fleet garage robotics landscape in 2026 is diverse and rapidly expanding. Different robots serve different functions, and a well-equipped garage may deploy several types working in coordination. Here is what is available and where each type fits into the maintenance workflow:
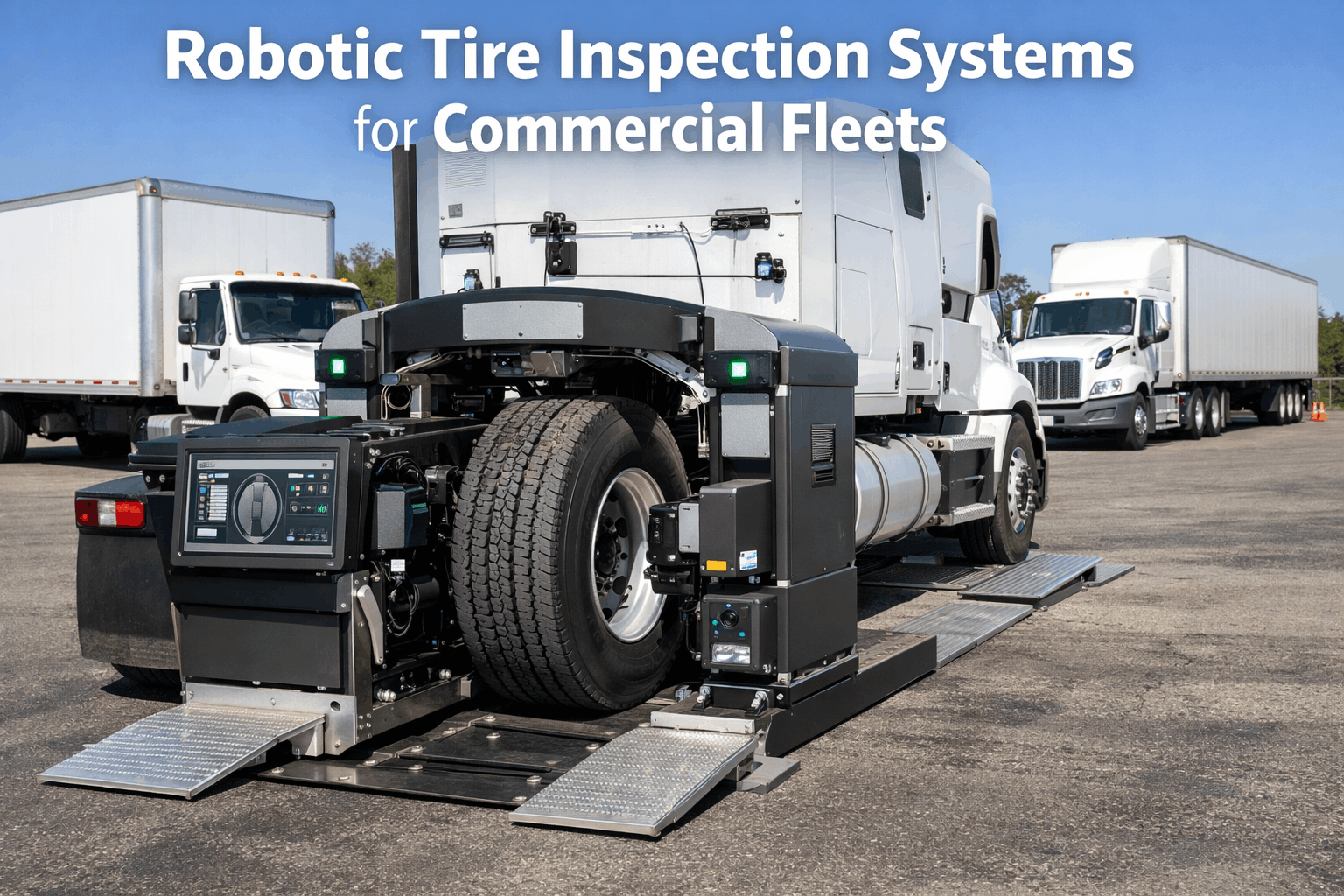
AI Vision Inspection Systems
These systems use high-resolution cameras, LiDAR, and machine learning to perform rapid, comprehensive vehicle inspections. Systems like UVeye's Helios can scan a vehicle's exterior and undercarriage in under five minutes, detecting damage, corrosion, fluid leaks, tire wear, and structural defects with accuracy that exceeds manual inspection. They generate detailed digital reports that feed directly into your CMMS for work order creation.
Robotic Tire and Fluid Service Arms
Robotic arms equipped with RFID scanning and precision tooling can mount, balance, and replace tires autonomously. They identify correct tire specifications by scanning the vehicle, select the right tire from inventory, and complete the swap without technician intervention. Similar systems handle fluid exchanges — oil, coolant, brake fluid, and transmission fluid — with precise measurement and zero-spill operation.
AI Diagnostic Robots
These robots connect to a vehicle's OBD-II port or CAN bus system and use AI to analyze engine performance, emissions data, electrical systems, and sensor health in real time. They identify anomalies, predict potential failures, and generate diagnostic reports that pinpoint root causes rather than just fault codes. This transforms diagnostics from reactive troubleshooting into predictive intelligence.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
AMRs navigate the garage floor autonomously, transporting parts, tools, and supplies between storage areas and service bays. They use SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) technology to navigate around obstacles, vehicles, and people. In high-volume fleet garages, AMRs eliminate the time technicians spend walking to parts rooms and carrying heavy components, keeping them focused on the vehicle in front of them.
Battery Inspection and Swap Robots
As electric vehicle fleets grow, specialized robots handle battery health diagnostics, thermal imaging of battery packs, and automated battery swapping for vehicles designed with swappable architectures. These systems measure voltage, internal resistance, and temperature distribution across battery cells, identifying degradation before it affects range or performance.
Cobots (Collaborative Robots)
Cobots work directly alongside human technicians, assisting with tasks that require both robotic precision and human judgment. They feature force-limiting sensors and speed monitors that allow safe operation in shared spaces. In fleet garages, cobots assist with brake component installation, suspension work, and other tasks where a steady robotic arm complements a technician's expertise.
Connect Your Robots to Your Maintenance Workflow
Autonomous robots generate data. Oxmaint turns that data into work orders, compliance records, and actionable maintenance intelligence. Bridge the gap between robotic automation and fleet maintenance management.
Why CMMS Integration Is Non-Negotiable for Robotic Garages
An autonomous robot performing a vehicle inspection produces a detailed digital report. A diagnostic robot generates fault predictions and component health scores. A tire-changing robot logs every swap with torque values and tire specifications. But without a CMMS to receive, organize, and act on this data, it sits in isolated silos — disconnected from your maintenance schedules, technician assignments, parts inventory, and compliance documentation. The result is a technologically advanced garage that still operates with fragmented workflows and manual coordination.
Oxmaint serves as the central nervous system that connects every autonomous robot in your garage to a unified maintenance management platform. Here is how the integration works across the maintenance lifecycle:
Robot Performs Task
An AI inspection robot scans a fleet vehicle and detects brake pad wear below threshold, a slow tire leak, and early corrosion on the undercarriage. The diagnostic robot simultaneously identifies a pending catalytic converter efficiency fault from the engine management system.
Data Flows to Oxmaint
The robot's findings are transmitted to Oxmaint automatically via API integration. Each finding is categorized by severity, component, and recommended action. The system matches the vehicle to its asset profile, pulling in maintenance history, warranty status, and scheduled service records.
Work Orders Auto-Generate
Oxmaint creates prioritized work orders for each identified issue. Brake pad replacement is flagged as urgent, the tire repair is scheduled for the next available bay, and the undercarriage corrosion is logged for preventive treatment during the vehicle's next scheduled service window.
Tasks Are Assigned and Tracked
Work orders are automatically assigned to available technicians based on skill set, certification, and current workload. Parts are checked against inventory — if brake pads are in stock, the work order proceeds; if not, Oxmaint triggers a purchase order automatically. Every step is tracked in real time.
Complete Documentation
When the work is completed, all robot-generated inspection data, technician actions, parts used, and time spent are consolidated into a single maintenance record. This record is available for compliance reporting, fleet analytics, and future predictive maintenance reference.
This closed-loop workflow eliminates the manual handoffs, paper-based reporting, and communication gaps that slow down fleet maintenance operations. Sign up for Oxmaint to start building automated maintenance workflows for your fleet garage.
Real-World Applications Shaping Fleet Garages in 2026
The convergence of robotics, AI, and fleet management is not theoretical — it is happening now across multiple industry segments. Here is how autonomous maintenance robots are being deployed in real fleet operations:
Large trucking fleets are deploying undercarriage inspection robots at terminal entry points. Every truck returning from a route passes through an automated scan that checks for brake wear, air leak indicators, tire condition, and structural damage. Findings are pushed to the fleet's CMMS, and vehicles with critical findings are flagged before their next dispatch — preventing roadside breakdowns and DOT violations.
Municipal bus fleets are using overnight robotic inspection systems that scan parked buses during off-hours. By the time morning operations begin, every vehicle has a current condition report, and work orders for any needed repairs are already queued for the maintenance team. This eliminates the morning rush to manually check buses before they enter service.
EV fleet operators are leveraging battery diagnostic robots that perform thermal imaging and cell-level health assessments during routine charging windows. These systems detect battery degradation patterns weeks before they affect range, allowing proactive battery conditioning or replacement scheduling that keeps the fleet at peak performance.
Construction fleet garages are deploying AMRs to transport heavy components like hydraulic cylinders, brake assemblies, and engine parts between storage and service bays. Cobots assist technicians with heavy lifting and precision installation tasks. AI diagnostic systems monitor telematics data from the field and pre-stage work orders before equipment returns to the shop. Book a demo to see how Oxmaint supports heavy equipment fleet maintenance.
Preparing Your Fleet Garage for Autonomous Robots
Adopting autonomous maintenance robots is not a switch you flip overnight. It requires strategic planning across technology, infrastructure, workforce, and systems integration. Here is a practical roadmap for fleet managers planning their robotics adoption in 2026:
Establish Your Digital Foundation
Before any robot rolls into your garage, you need a CMMS that can receive and process the data they generate. Implement Oxmaint to digitize your asset records, maintenance histories, parts inventory, and work order workflows. This digital foundation is what robots will connect to, and without it, robotic data has nowhere productive to go. Sign up now to build your digital foundation.
Start with Inspection Automation
AI vision inspection systems offer the fastest ROI with the lowest disruption. They do not replace technicians — they enhance the inspection process by catching defects that human eyes miss and reducing inspection time from hours to minutes. Their output feeds directly into Oxmaint as actionable findings.
Add Logistics and Parts Delivery Robots
AMRs that transport parts and tools between storage and service bays are the next logical step. They reduce non-productive technician movement, improve parts tracking accuracy, and integrate with your CMMS inventory management to maintain real-time stock visibility.
Deploy Servicing and Diagnostic Robots
Once your digital infrastructure and logistics automation are stable, introduce robotic arms for repetitive servicing tasks and AI diagnostic systems for predictive fault detection. These systems generate the highest volume of maintenance data, which Oxmaint processes into work orders, trend reports, and predictive analytics.
Scale and Optimize
Use Oxmaint's analytics dashboards to measure robot performance, technician productivity, and overall garage efficiency. Identify bottlenecks, optimize task allocation between robots and humans, and expand robotic capabilities based on data-driven decisions rather than assumptions.
Build the Fleet Garage of Tomorrow with Oxmaint
Whether you are deploying your first inspection robot or scaling a fully automated workshop, Oxmaint is the CMMS platform that connects robotic intelligence to fleet maintenance operations. Start today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are autonomous maintenance robots for fleet garages
Autonomous maintenance robots are AI-enabled machines that perform inspection, diagnostic, and routine servicing tasks on fleet vehicles with minimal human intervention. They include AI vision inspection systems, robotic servicing arms, diagnostic robots, autonomous mobile robots for parts delivery, and collaborative robots that work alongside technicians. These systems use machine learning, computer vision, and IoT connectivity to operate independently while reporting their findings to a CMMS.
Will autonomous robots replace fleet technicians
No. Autonomous robots handle repetitive, time-consuming, and physically demanding tasks, freeing technicians to focus on complex diagnostics, critical repairs, and decision-making that requires human expertise. The role of the technician evolves from manual labor toward higher-value work including robot supervision, data interpretation, and advanced troubleshooting. Fleets that adopt robotics report higher technician satisfaction because the most tedious parts of the job are automated.
Why does a robotic fleet garage need a CMMS like Oxmaint
Robots generate enormous amounts of inspection, diagnostic, and servicing data. Without a CMMS, this data remains in isolated silos disconnected from your maintenance schedules, work orders, parts inventory, and compliance documentation. Oxmaint receives robot-generated data, automatically creates prioritized work orders, assigns tasks to technicians, tracks parts usage, and maintains complete maintenance records. It is the system that turns robotic intelligence into operational action.
What types of fleet garages benefit most from autonomous robots
High-volume fleet garages with 50 or more vehicles see the fastest ROI from autonomous maintenance robots. This includes trucking and logistics operations, transit agencies, delivery fleets, construction equipment yards, and rental fleet maintenance facilities. However, mid-size fleets can start with AI inspection systems and AMRs for parts logistics to achieve significant efficiency gains at lower investment levels.
How do autonomous robots integrate with Oxmaint
Robots connect to Oxmaint through API integration. When a robot completes an inspection, diagnostic scan, or servicing task, its findings and completion data are transmitted to Oxmaint automatically. The CMMS then processes this data according to your configured rules — creating work orders, updating asset records, triggering parts orders, and notifying the appropriate personnel. No manual data entry is required.
What is the cost of implementing autonomous maintenance robots
Costs vary significantly based on the type and scale of deployment. AI vision inspection systems can start in the tens of thousands of dollars range, while full robotic servicing arms for tire or fluid services represent larger investments. However, the ROI calculation should account for reduced downtime, fewer missed defects, lower labor costs on repetitive tasks, and faster vehicle turnaround times. Most fleets report positive ROI within the first 12 to 18 months of deployment.
How quickly can a fleet garage implement Oxmaint for robotic integration
Oxmaint is cloud-based and can be operational within two to three weeks for standard fleet maintenance management. Robotic integration timelines depend on the specific robot manufacturer's API capabilities, but most modern autonomous maintenance robots are designed with open APIs that connect to CMMS platforms like Oxmaint. Your fleet can begin digitizing maintenance workflows immediately while planning robotic deployments in parallel.